Blood clots: invisible and dangerous to health and life. How to minimize risks
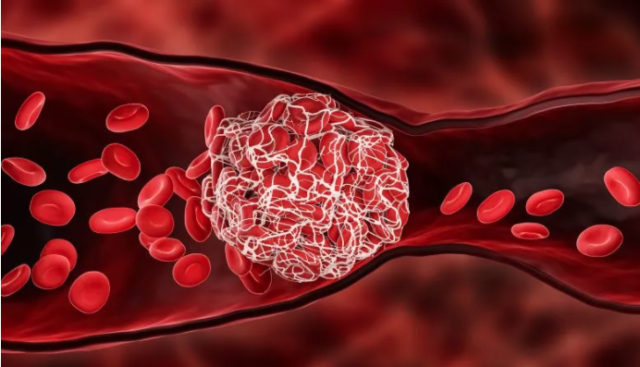
Why do blood clots form in blood vessels?
A blood clot is a blood clot that appears in the lumen of a blood vessel or heart cavity. The danger is that it can grow, block a vessel or “break off”, this is called a thromboembolism.
There are several causes of blood clots, and not all of them can be controlled. For example, a bleeding disorder occurs due to genetic defects or autoimmune diseases. They are hereditary or acquired. Also, pregnancy and the postpartum period sometimes affect blood clotting. This is due to an increase in progesterone levels, which affects the viscosity of the blood.
Why do blood clots form in blood vessels?
A blood clot is a blood clot that appears in the lumen of a blood vessel or heart cavity. The danger is that it can grow, block a vessel or “break off”, this is called a thromboembolism.
There are several causes of blood clots, and not all of them can be controlled. For example, a bleeding disorder occurs due to genetic defects or autoimmune diseases. They are hereditary or acquired. Also, pregnancy and the postpartum period sometimes affect blood clotting. This is due to an increase in progesterone levels, which affects the viscosity of the blood.
Thrombus formation factors
An increased risk of blood clots is caused by:
- genetic inheritance to predisposition;
- diseases that limit physical activity, such as adherence to bed rest;
- arrhythmia and diseases that disrupt the rhythm of the blood circulation in the system;
- varicose veins;
- liver dysfunction;
- alcoholism;
- high body mass index;
- age-related changes in hormone levels;
- smoking;
- diabetes;
- unhealthy diet, which affects fat metabolism; the risk of atherosclerosis and thrombosis increases each increase in total cholesterol concentration by 10 mg/dl;
- frequent injury, hypothermia, or overheating;
- dehydration of the body;
- high slagging;
- deficiency of the vitamin and mineral complex;
- hypoxia;
- high cholesterol levels;
- stress.
Some cannot be influenced, but quality prevention, such as nutrition and physical activity, can minimize the effects of a blood clot.
Causes of blood viscosity
There is no concept of “blood thinning” in medicine. Doctors call this “coagulation reduction”. Unpleasant, but common diseases, such as stroke, heart attack, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, arise, among other things, due to thick blood.
Blood-thinning occurs due to the increased amount of water in the peripheral blood. It should circulate freely through the blood vessels, and not pass like a thick jelly.
Prevention of vascular thrombosis
- go in for sports or physical activity to keep the body and blood vessels in good shape, especially when sedentary work; do exercises, walk around the office, swim, run;
- walk in the fresh air, which enriches the blood with oxygen;
- refuse or minimize bad habits;
- do not wear tight, tight clothing;
- you can take medicines to thin the blood, but only after consulting a doctor;
- eat healthy foods that have a positive effect on blood thinning.
Foods that thicken the blood
Sugar, fatty foods, meat products and offal (especially liver), dairy products, walnuts, legumes, bananas, alcohol, fatty cheeses, fatty dairy products, butter, smoked meats, sausages, dried and salted fish, chips, fast food, lemonade and soda, sweets, milk chocolate, pastries, fatty sauces.
Blood-thinning foods
- food should be balanced in terms of parameters – proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals;
- the diet should be predominantly vegetable with a lot of greens and fiber;
- meat: lean varieties, turkey or chicken;
- fish: seafood and lean;
- seafood – contains taurine, which is important for the body;
- fermented milk products and eggs;
- vegetables: baked potatoes, tomatoes, cabbage, beets, red bell peppers;
- fruits: grapefruit, melon, pomegranate (in small quantities so as not to increase hemoglobin), lemon, orange, sour apples;
- berries: blueberries, viburnum, currants, sea buckthorn, raspberries, cranberries;
- decoctions from plants: birch, willow bark, common onion, sweet clover, chestnut, chamomile, St. John’s wort, string, meadow clover flowers, the rhizome of Valerian officinalis; you can additionally drink elderberry broth, dandelion juice, willow bark, ginkgo Biloba;
- birch buds, linden leaves, and color, hawthorn, dill, rose hips can also strengthen arteries, veins, capillaries;
- oils: olive, linseed, sea buckthorn, sesame;
- add bitter and common spices to dishes: garlic, ginger, cinnamon, milk thistle;
- drink water: pure still, with magnesium, taurine;
- drinks: green tea, rooibos, hibiscus, chicory, herbal teas.
Additionally
Treatments with leeches, which produce hirudin in their saliva, are also helpful. The enzyme blocks thrombus formation in both large and small vessels, lengthens the blood coagulation time, prothrombin time.
Important: you can not overdo it in the blood-thinning procedure. Before self-medication, you need to visit a doctor and get professional advice and, possibly, undergo specific examinations or tests.